A Tale of Deceptive Design: The Rise of Dark Patterns in E-commerce
In the vast world of e-commerce, dark patterns emerged as a sneaky tactic to manipulate users into making decisions that benefited the platform, rather than the user. These deceptive design techniques, such as bait and switch, urgency, and forced continuity, exploited human vulnerabilities and cognitive biases to drive impulsive purchases and subscriptions. As consumers became increasingly aware of these tactics, they began to distrust the platforms, leading to a decline in user satisfaction and loyalty. Governments and regulatory bodies, recognizing the potential harm caused by dark patterns, took action to protect consumers. The Indian government, for example, banned the use of dark patterns on e-commerce platforms and issued guidelines to prevent their deceptive use. These guidelines aimed to ensure transparency and fairness in e-commerce interactions, paving the way for a more trustworthy online shopping experience. E-commerce businesses eager to maintain their customers’ trust and loyalty began to prioritize user experience, transparency, and honesty. They realized that by providing clear and accurate information, obtaining genuine user consent for transactions, and avoiding manipulative tactics that exploited user vulnerabilities, they could build long-term relationships with their customers. This approach marked a significant shift in the e-commerce landscape, as businesses focused on creating a more user-centric and trustworthy online shopping environment. As dark patterns continue to rise and evolve, the fight against deceptive design practices will remain a top priority for governments, regulators, and e-commerce platforms. By understanding and addressing dark patterns, the e-commerce industry can work together to create a more transparent, trustworthy, and user-friendly online shopping experience for all.
Understanding Dark Patterns in E-commerce
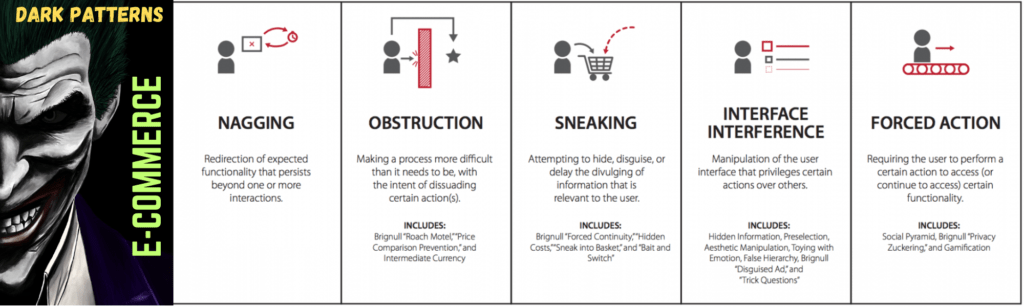
Dark patterns encompass various design tactics employed by e-commerce platforms to influence user behavior. These tactics often exploit cognitive biases and user psychology to encourage actions such as making unintended purchases, providing personal information, or subscribing to services. Some common types of dark patterns include:
- Bait and Switch: This involves advertising a product or service at a certain price, only to reveal a different, usually higher price upon interaction.
- Urgency: Creating a false sense of urgency to prompt immediate action, such as making a purchase, by displaying misleading countdowns or stock availability.
- Forced Continuity: Automatically adding extra items or services to a user’s cart, often with pre-selected checkboxes, leading to unintended purchases.
- Misleading Information: Presenting false or exaggerated information about a product or service to influence user decisions.
- Scarcity: Exaggerating the limited availability of a product to encourage quick purchases.
Impact on Consumers
Dark patterns can have significant negative effects on consumers. They can lead to financial harm, erode trust in e-commerce platforms, and cause frustration and dissatisfaction among users. By exploiting cognitive vulnerabilities, these patterns can manipulate users into actions that do not align with their genuine preferences, leading to a sense of being deceived.
Regulatory Response
Recognizing the potential harm caused by dark patterns, some governments and regulatory bodies have taken steps to address this issue. For instance, the Indian government has banned the use of dark patterns on e-commerce platforms and has issued guidelines to prevent their deceptive use. These guidelines aim to protect consumers from misleading practices and ensure transparency and fairness in e-commerce interactions.
Mitigating Dark Patterns
E-commerce businesses can take proactive measures to avoid the use of dark patterns. By prioritizing user experience, transparency, and ethical design, companies can build trust and long-term relationships with their customers. This approach involves providing clear and accurate information, obtaining genuine user consent for transactions, and avoiding manipulative tactics that exploit user vulnerabilities.In conclusion, dark patterns in e-commerce represent a significant challenge to consumer trust and online commerce integrity. By understanding these patterns, their impact, and the measures being taken to address them, businesses and regulatory authorities can work together to create a more transparent, ethical, and user-centric e-commerce environment.This article provides an overview of dark patterns in e-commerce, their impact on consumers, and the regulatory and industry responses to mitigate their use. By understanding and addressing dark patterns, e-commerce can evolve to be more transparent, trustworthy, and user-friendly.

